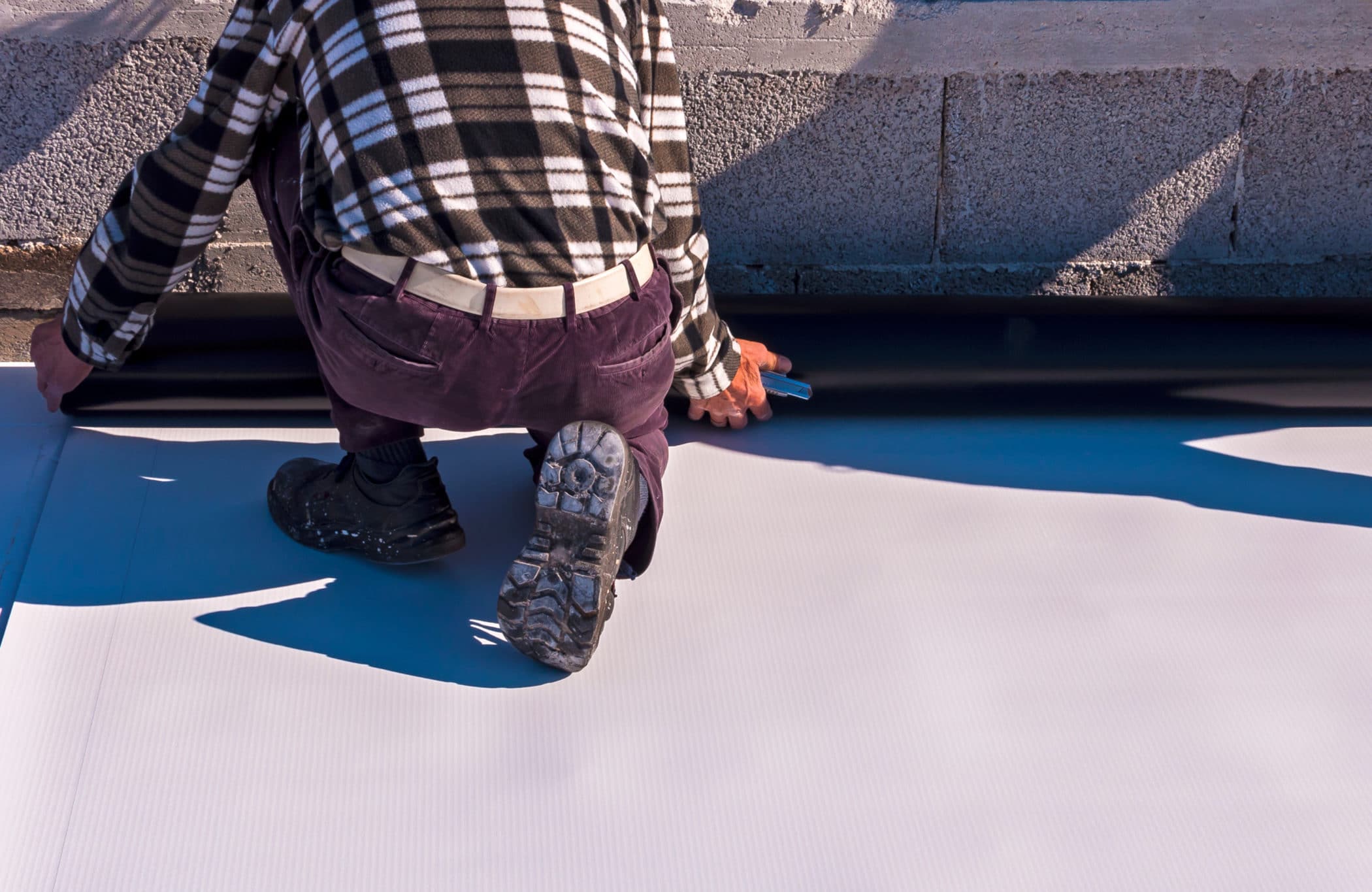
Now a coating acts as a barrier to help protect the roof from the elements. It does this by increasing the UV protection and to fight against the harmful rays produced by the sun. This can eventually help to reduce the building’s energy costs. A coating is also water-resistant, but not all sealants are the same. As with anything some materials are better than others when it comes to the prevention of ponding water. Applying a coating can be a cost-effective option over a full roof replacement. In order to determine this it is important to do your research and consider the condition of your roof, the location, the slope, and amount of exposure your roof has to chemicals, heat, and UV rays. Here are some comparisons of the strengths and weaknesses of each sealant coating. This might help determine which coating material is best for your next commercial roofing job.
Acrylic roof coatings
Acrylic is a water-based, cost-effective solution. They can be good for a variety of roofs. This coating is good for a lot of different climates and could provide the best value.
Strengths: Acrylic coatings can offer cost efficiency and great performance. They are actually highly reflective, are UV resistant, and very easy to work with.
Weaknesses: Acrylics will actually lose mil thickness with weathering. They also need to be applied at 50°F or above. Acrylic coatings also do not perform well in ponding-water situations.
Polyurethane roof coatings
Polyurethanes are more actually impact resistant and can handle traffic the best out of all coatings. There are two main types of coatings: aromatic and aliphatic. Aromatic coatings are less expensive and not UV stable. These are usually used as a base coating. Aliphaltic coatings on the other hand are more expensive, but they are UV stable. They also hold color well, and will stay cleaner than most other coatings.
Strengths: A urethane roof coating system with an aromatic base and an aliphatic top coat is not only durable, but will stay cleaner, and is more resistant to ponding water than an acrylic coating. They also will do well as a “cool roof” because they can be white and stay clean.
Weaknesses: They tend to be more expensive than acrylic coatings. They also can have a strong odor.
Silicone roof coatings
Silicones coatings actually cure in moisture and humidity. In some applications, you can eliminate the need for a primer.
Strengths: Silicones weather better than other coatings with almost no erosion and they don’t get hard or brittle. Silicone is also good in ponding water situations.
Weaknesses: Silicone coatings can hold dirt and rain and will act as a cleaner. Unfortunately because of this the material loses its reflectivity over time. It can also be hard to adhere to silicone. So when the time comes to have your roof re-coated, you must either remove the coating completely or re-coat with a compatible silicone. Also the resistance to tearing is a mechanical weakness and silicone coatings should be used with fabric.
As you can see there are many choices when it comes to coatings. Each have their benefits and downfalls. It is important to look at each option profusely as you might find a cost and energy efficient coating to be a better solution over a full roof tear-off and replacement.